Immediately After The Switch Is Closed What Is The Voltage Across The Capacitor Chegg | We can calculate the currents through each resistor by first calculating the total resistance This video explains the potential of a capacitor and how they function in a circuit. Show your solution.) what you want to understand is that an inductor creates a voltage to resist sudden changes in current. (a) find the time interval required for the capacitor to reach this charge. Homework statement the problem is:
The capacitor in the figure is initially uncharged. Capacitors store electrical energy on their plates in the form of an electrical charge. The voltage across each of the components in series is in the same proportion as their resistance: At a maximum and decreasing 3. 1 answer to the switch s in fig.
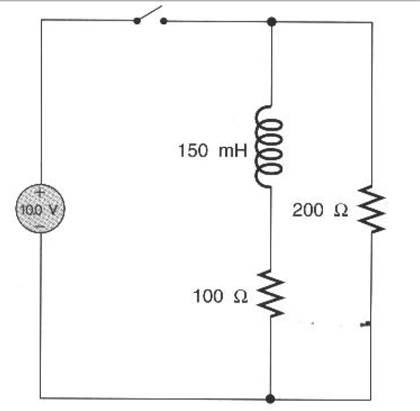
Immediately after the switch is closed, what is the current through the resistor r1? A big current) and this decreases as time goes. When a voltage is placed across the capacitor the potential cannot rise to the applied value instantaneously. D)after a very long time, what is the voltage across the capacitor? A capacitor of capacitance c = 3.5 uf is initially uncharged. The switch s is closed for a long time, and no voltage is measured across the capacitor. The switch is closed at t=o. Immediately after the switch is closed, what is the potential difference across the inductor? An ideal capacitor is characterized by a constant capacitance c, in farads in the si system of units a capacitance of one farad (f) means that one coulomb of charge on each conductor causes a voltage of one volt across the device.23 because the conductors (or plates) are close together, the. Correct while no charge can physically pass through the gap between the. When you switch a voltmeter from a lower to a higher voltage range, an additional resistor is added in series with the meter, increasing the voltage necessary to create the same voltage drop across or current flow through the. .after the switch is closed, what is the voltage drop vc, in volts, across the capacitor? Can you explain why the graphs are related in this way?
The only thing left to calculate is the emf e(t) across the generator. Part c immediately after the switch is closed, what is the direction of the current in the circuit? Voltage across c = voltage across r. Homework statement the problem is: A capacitor of capacitance c = 3.5 uf is initially uncharged.

Show your solution.) what you want to understand is that an inductor creates a voltage to resist sudden changes in current. When you switch a voltmeter from a lower to a higher voltage range, an additional resistor is added in series with the meter, increasing the voltage necessary to create the same voltage drop across or current flow through the. Before closing the switch that voltage was also 0. This video explains the potential of a capacitor and how they function in a circuit. Problem 2 20f 16 » constants immediately after the switch is closed, what is the voltage across the resistor? The voltage across each of the components in series is in the same proportion as their resistance: Consider a series circuit containing a initially, the switch is open and the capacitor discharged. Voltage across c = voltage across r. Immediately after the switch is closed, the capacitor acts like a short circuit for a very small time. It is connected in series. As the charge on the terminals builds up to its final when the switch is closed, and charging starts, the rate of flow of charge is large (i.e. After the switch is opened, the voltage across the capacitor find the current passing through battery immediately after key (k) is closed. (c) what is the current in the inductor after the switch has been closed for a long time?
If the switch is closed (connected) the voltage across it will read 0v. • just after the switch is thrown, the capacitor still has no charge, therefore the voltage drop across the capacitor = 0! The general graph of voltage across a capacitor as it is charged is shown in the figure below: Determine the current, i(t), when the capacitance is c = 0.125 f and the voltage is v(t) = 12 cos(2t + 30°) v. The only thing left to calculate is the emf e(t) across the generator.
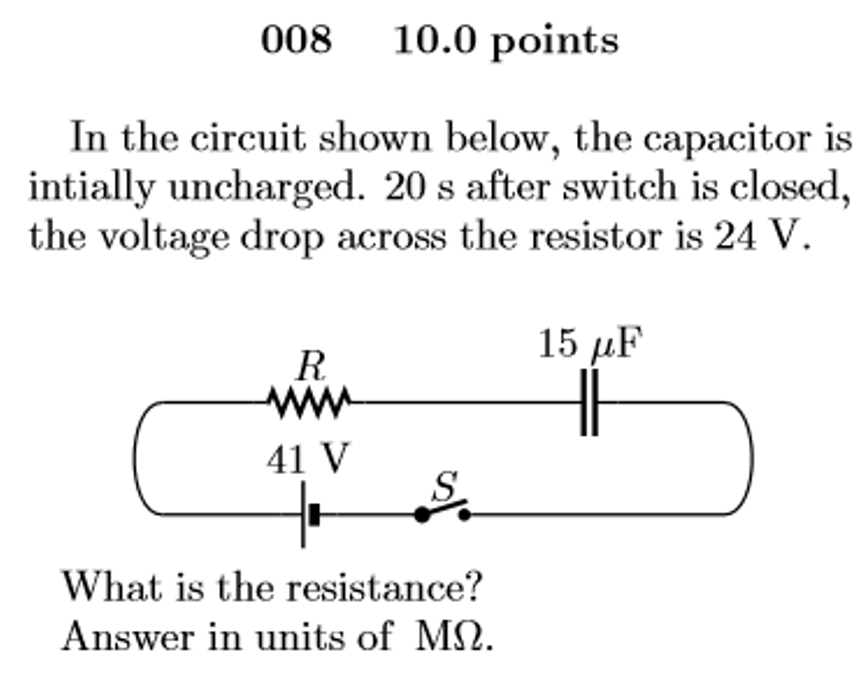
The voltage across each of the components in series is in the same proportion as their resistance: Can you explain why the graphs are related in this way? A big current) and this decreases as time goes. The switch is closed at t=o. Immediately after the switch is closed, the initial current is io =vo /r=10v/10ω. The capacitor in the figure is initially uncharged. These are simulation results, but we can use some basic scientific principles to understand and predict the voltage across therefore the voltage across the open switch is the same as the battery voltage When the switch is closed, charges immediately start flowing onto the plates of the capacitor. (a) 0 v (b) 9 v (c) 0.9 v. If the switch is now moved from position a to position b, the fully charged capacitor would start to discharge through the lamp now connected across it, illuminating the lamp until the capacitor. The switch is closed at t=0. The following circuits shows the voltage across open and closed switches in a 12v circuit: When a voltage is placed across the capacitor the potential cannot rise to the applied value instantaneously.
A big current) and this decreases as time goes immediately after the switch is closed what is the voltage across the capacitor. Homework statement the problem is:
Immediately After The Switch Is Closed What Is The Voltage Across The Capacitor Chegg: Clockwise counterclockwise there is no current because the capacitor does not allow the current to pass through.

Post a Comment